Published on 7 March 2024
VDMA 24994: new requirements for safe lithium-ion battery storage

Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly playing a pivotal role across numerous sectors. Consider the e-bikes and scooters in the recreation and home delivery industries, or the battery-powered tools and hand scanners in landscaping and logistics.
Safely charging these power sources is now more important than ever. Fires caused by lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly common. With the introduction of the VDMA 24994 whitepaper, we are taking a significant step forward in protecting against the risks of battery fires.
In this blog, we delve deeper into what VDMA 24994 entails and why it is crucial for entrepreneurs who work with these batteries daily.
What is VDMA 24994?
VDMA 24994 is a document that outlines the requirements for a battery safe to store and charge lithium-ion batteries safely. European certification bodies ESSA and ECB-S have joined forces for this initiative.
Is VDMA 24994 a European standard?
Why is VDMA 24994 necessary?
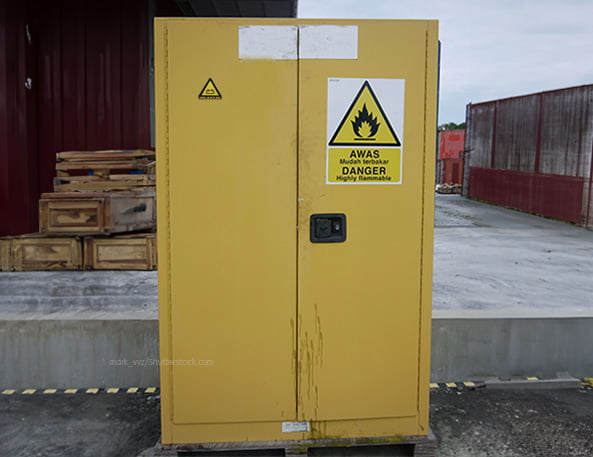
The need for a clear document like VDMA 24994 arises from practical experience. Many existing solutions, such as EN 14470-1 chemical cabinets, do not provide the necessary safety in the event of a battery fire. Incidents where batteries become extremely hot and ignite lead to situations where flames shoot out of the cabinet and doors burst open, with all the ensuing consequences.
Make sure to seek proper advice from experts and your insurer when purchasing a battery safe, as the wrong choice can have serious consequences. How can you be sure that a battery safeis truly secure? In our blog ‘How to choose a secure battery safe,’ we provide useful tips and explain what to look out for.

Key elements of VDMA 24994
VDMA 24994 sets clear requirements for the performance of lithium-ion battery cabinets. For example, these cabinets must be able to withstand certain temperatures and the forces of a potential explosion.
Additionally, supplementary safety requirements have been formulated. For instance, the doors of the battery safe must always be closed after a few minutes, because only then can a fire be contained within the safe. This can be achieved through an alarm that warns the doors are still open, or by self-closing doors.
The aim is to keep a battery fire within the safe and prevent it from spreading, while safely venting toxic smoke gases outside.
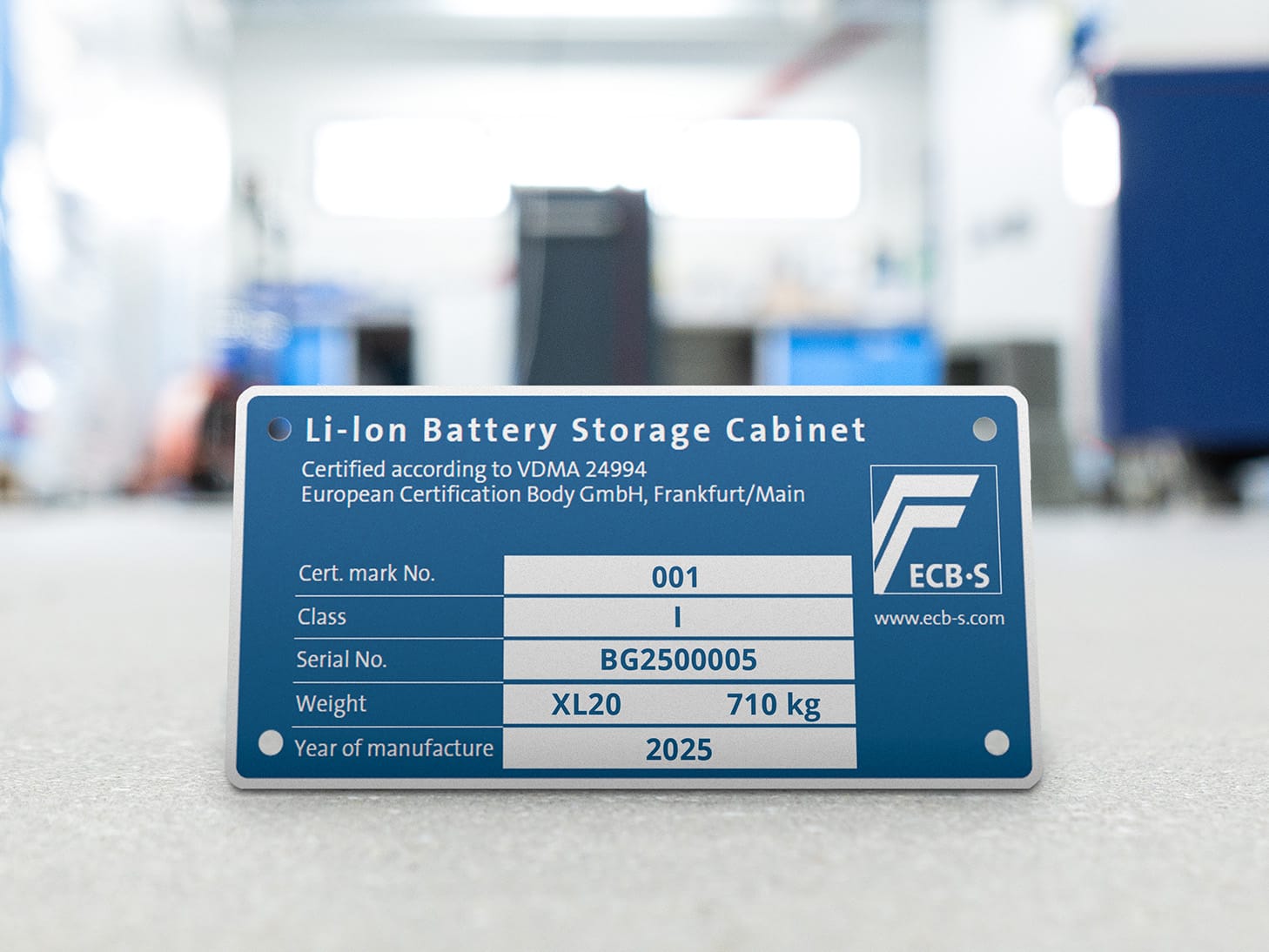
Batteryguard XL tested in preparation for VDMA 24994
Batteryguard XL served as a model in drafting the design requirements for VDMA 24994. In this context, Batteryguard was also been extensively tested by the renowned test institute MPA Dresden (Kiwa group) and the safe has proven to meet our specified requirements.
This provides business owners with the assurance that they are choosing a safe and reliable solution for their battery storage.
Want to know more about VDMA 24994?

If you want to learn more about how you can protect your business from the risks of lithium-ion battery fires, please contact our team or download our whitepaper.
Curious about all the possibilities?
Our safes specialists will be happy to advise you on our Batteryguard battery cabinets.